Workshop Exercise - Your Lab Environment
Table of Contents
Objectives
- Understand the lab topology and how to access the environment
- Understand how to perform the workshop exercises
- Understand challenge labs
Guide
Your Lab Environment
The workshop is provisioned with a pre-configured lab environment. You will have access to a host deployed with Ansible Automation Platform (AAP) which you will use to control the playbook and workflow jobs that automate the CentOS conversion workflow steps. You will also have access to three CentOS hosts. These are the hosts where we will be converting the CentOS operating system (OS) to Red Hat Enterprise Linux.
| Role | Inventory name |
|---|---|
| Ansible Automation Platform controller | ansible-1 |
| Satellite Server | satellite |
| Managed Host 1 - RHEL | node1 |
| Managed Host 2 - RHEL | node2 |
| Managed Host 3 - RHEL | node3 |
| Managed Host 4 - CentOS/OracleLinux | node4 |
| Managed Host 5 - CentOS/OracleLinux | node5 |
| Managed Host 6 - CentOS/OracleLinux | node6 |
Step 1 - Access the AAP Web UI
The AAP Web UI is where we will go to submit and check the status of the Ansible playbook jobs we will use to automate the CentOS conversion workflow.
-
Let’s open the AAP Web UI in a new web browser tab using the “Console” link under “Red Hat Ansible Automation Controller” on the workshop launch page. For example:
-
Enter the username
adminand the password provided. This will bring you to your AAP Web UI dashboard like the example below: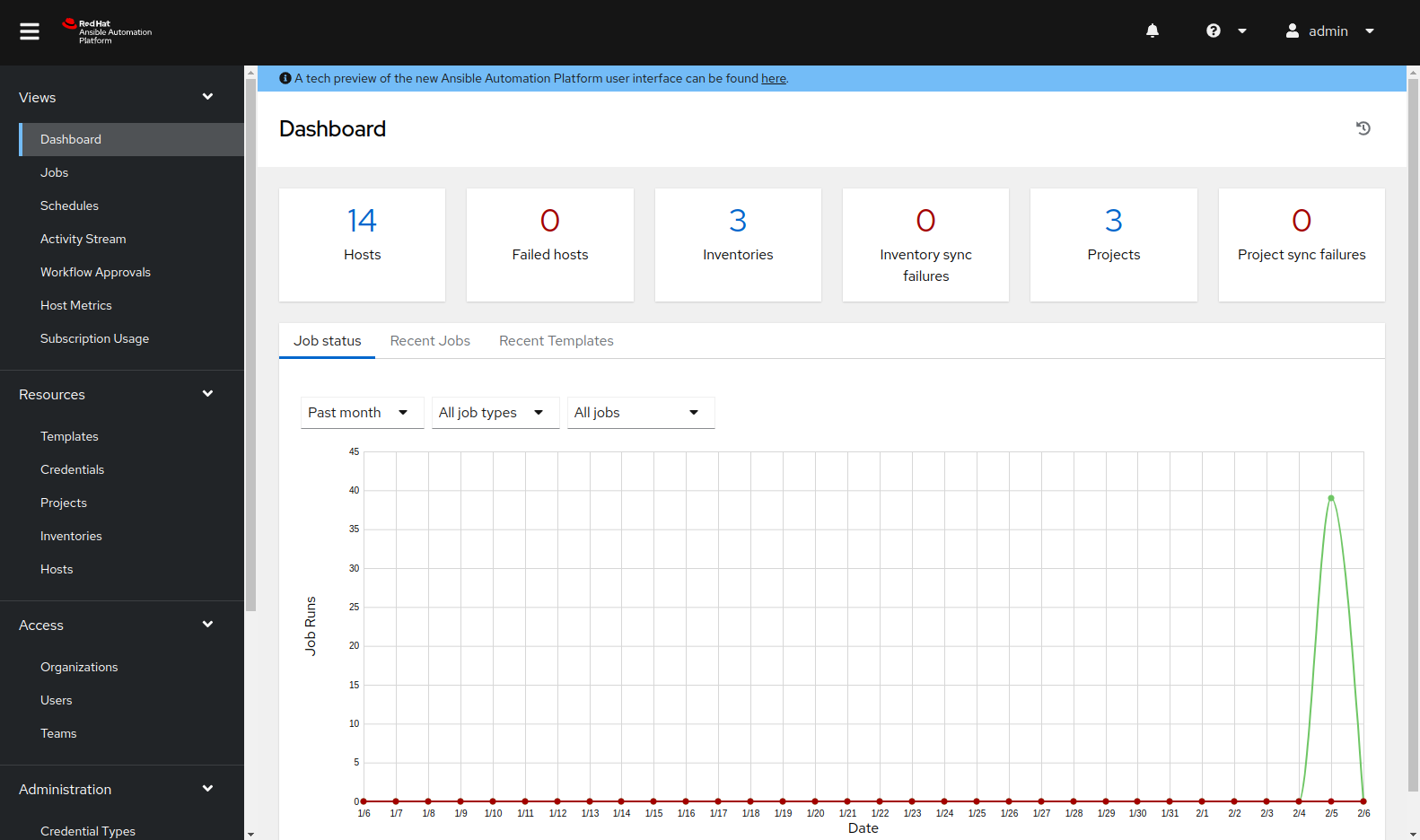
-
Let’s use the AAP Web UI to make a couple of preparations for the exercise. First, let’s ensure our CentOS nodes are up and running. In the AAP Web UI browser tab, navigate to Resources > Templates by clicking on “Templates” under the “Resources” group in the navigation menu. Browse the list of job templates and click on the template
EC2 / Instance action: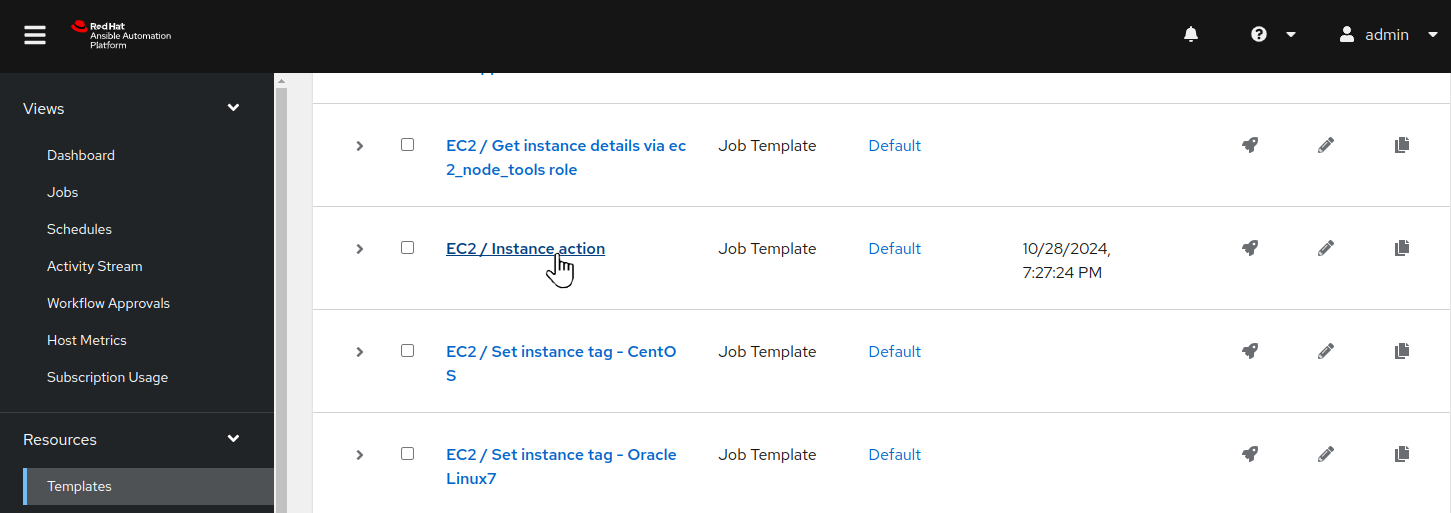
-
Review the job details and then click on
Launch: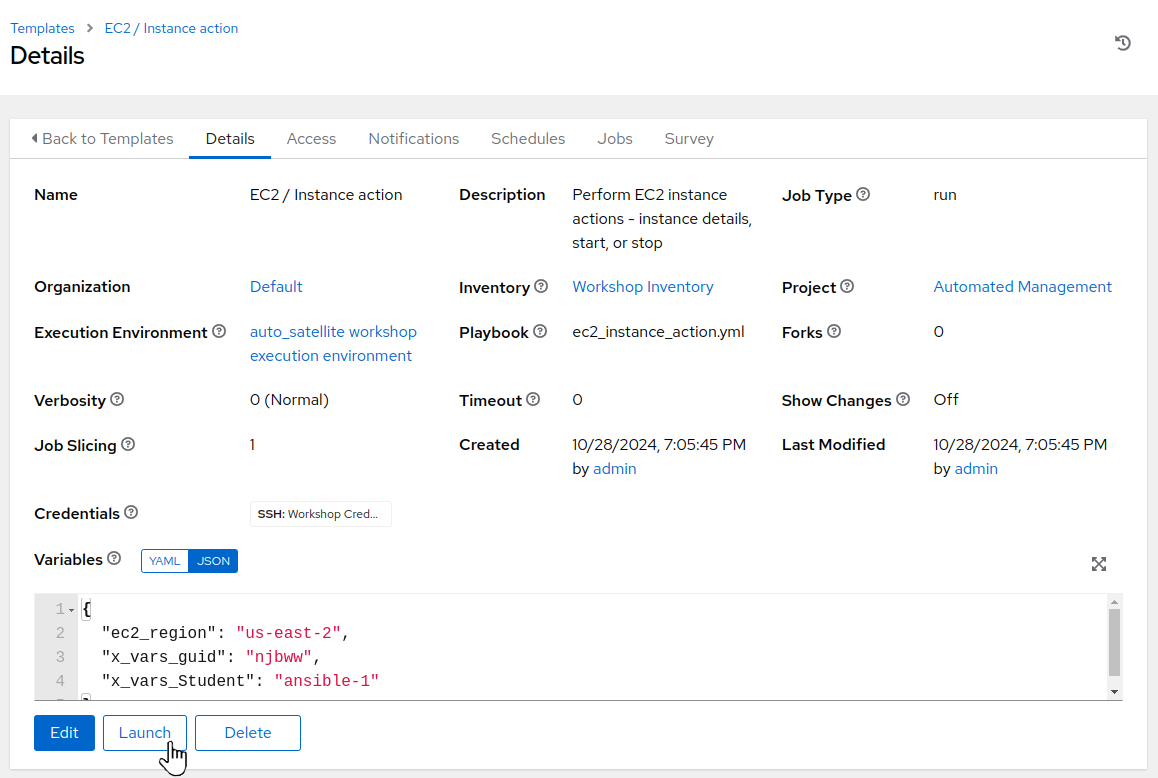
-
Review the job variables prompt and then click
Next: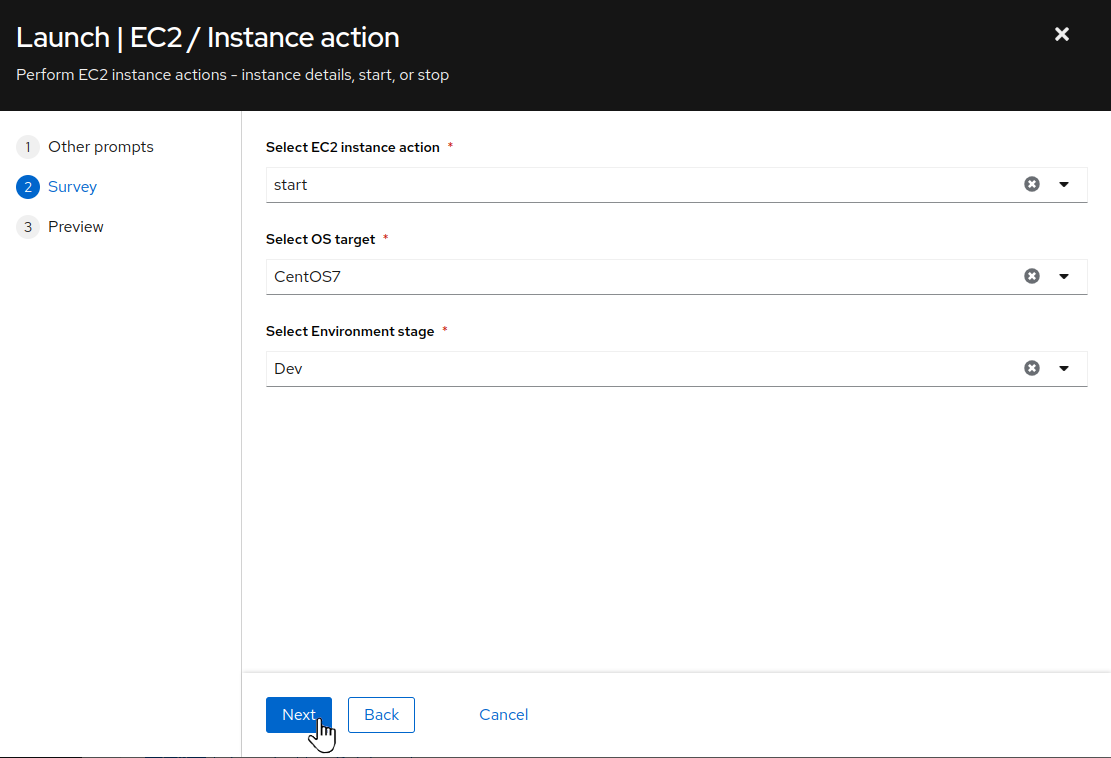
-
For
Select EC2 instance actionchoosestartfrom the drop down menu. ForSelect OS targetchooseCentOS7from the drop down. Finally, forSelect Environment stagechooseDevfrom the drop selection. Once the survey selections have been completed, clickNext:
-
Review the preview job dialog then click
Launch: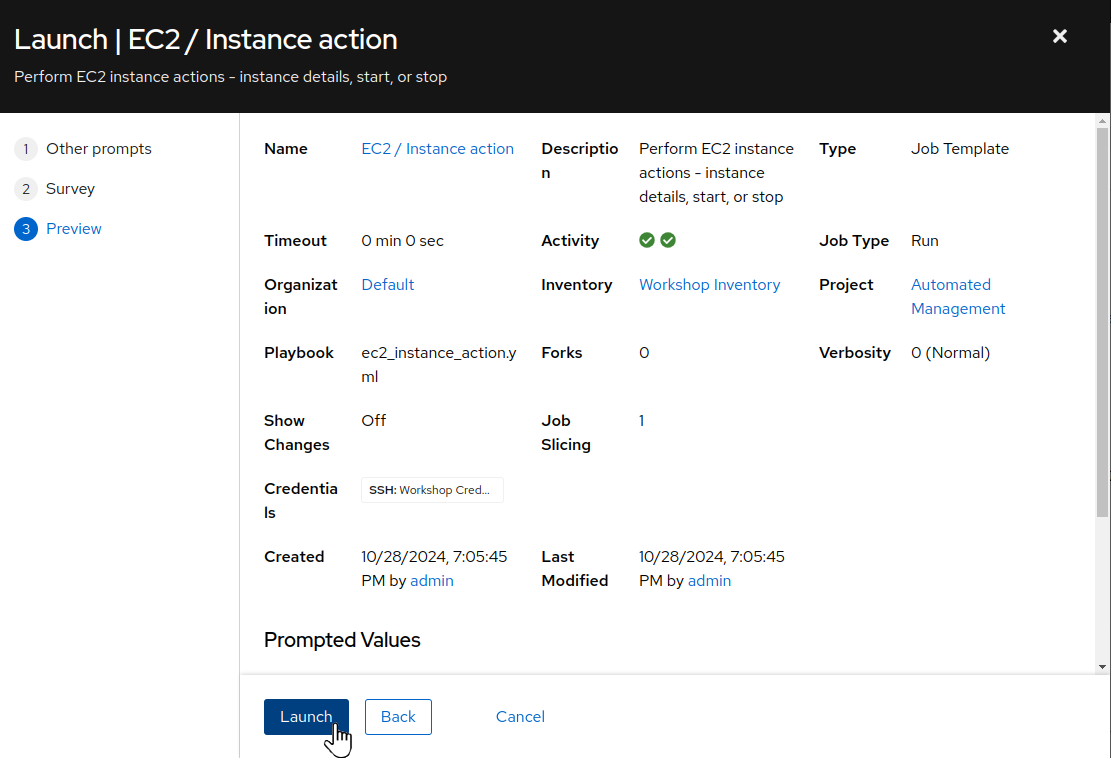
-
Verify that the job run is successful via the job output:
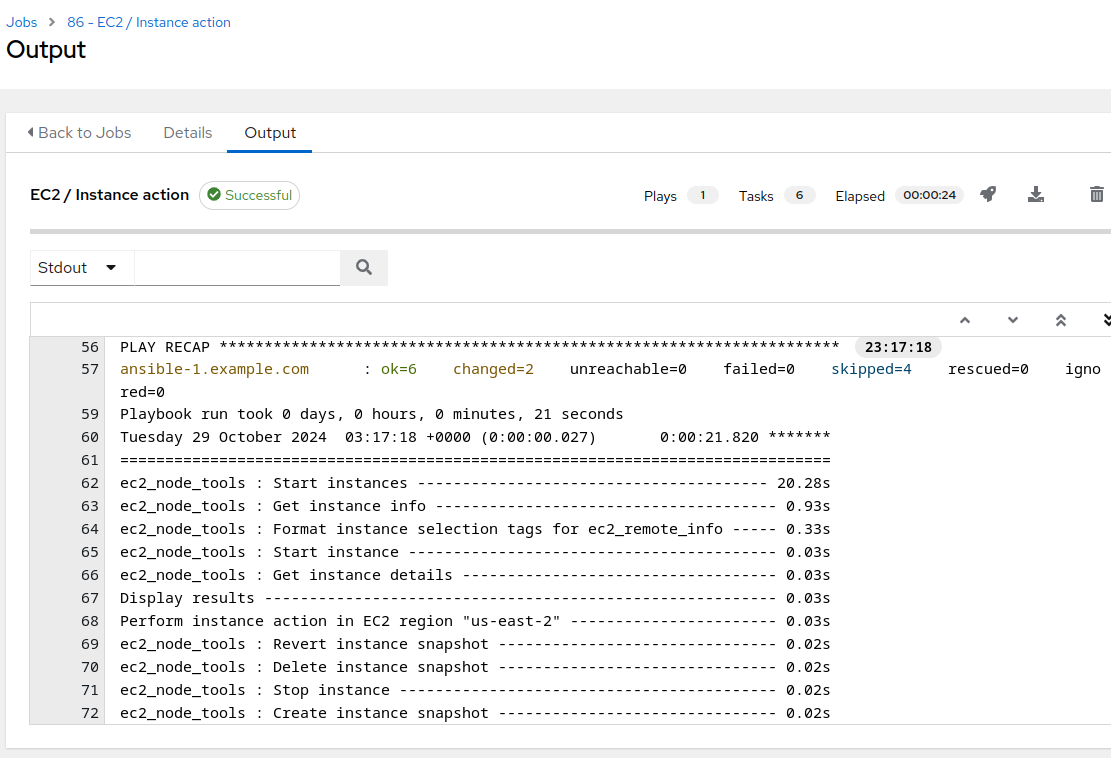
Additionally, we need to run some automation to make some final adjustments to the environment for the CentOS to RHEL conversion.
-
In the AAP Web UI browser tab, navigate to Resources > Templates by clicking on “Templates” under the “Resources” group in the navigation menu. Browse the list of job templates and click on the
 icon to the right of
icon to the right of Z / CaC / Controller / C2R - RIPU scenario: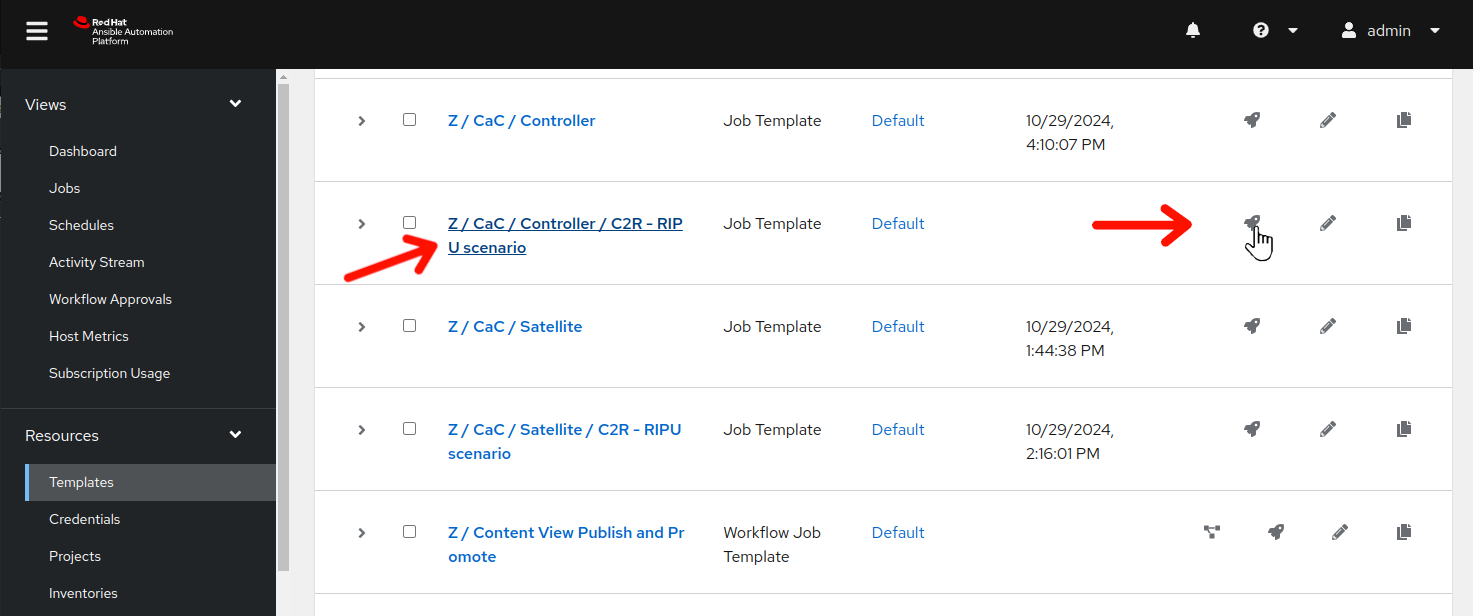
-
Review the job variables prompt and then click
Next: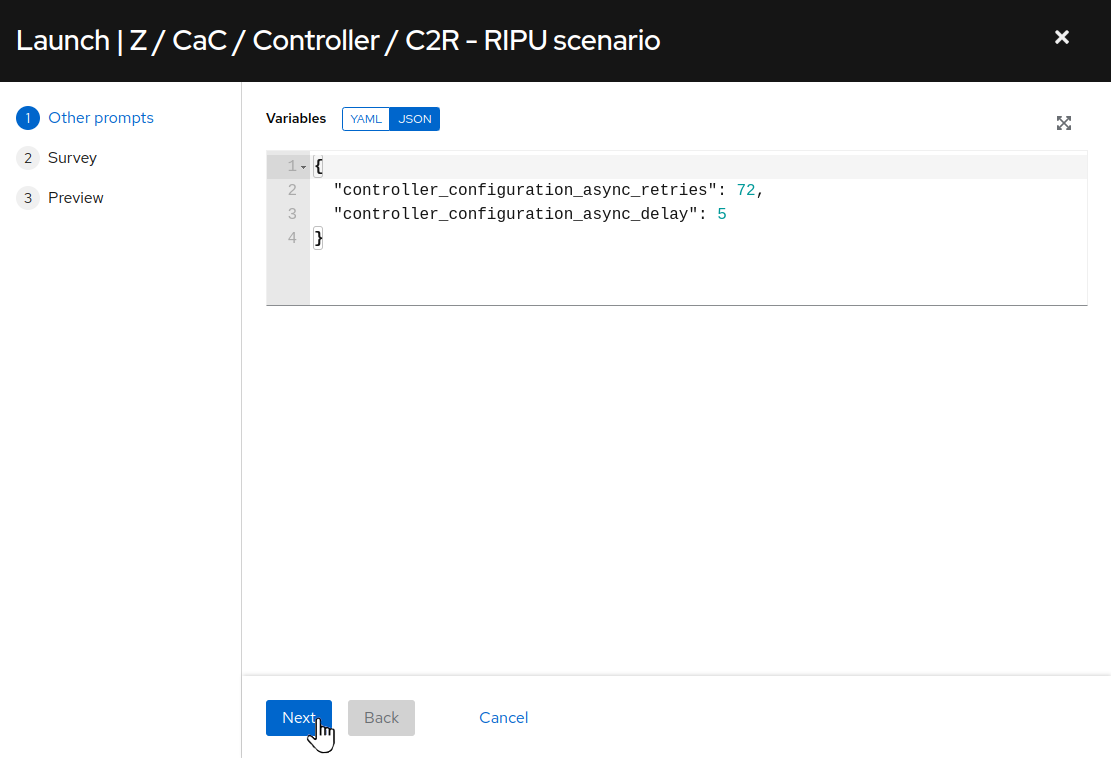
-
On the survey dialog, for
Choose C2R/RIPU version to prepare on ControllerchooseCentOS7_C2Rfrom the drop down menu. then clickNext: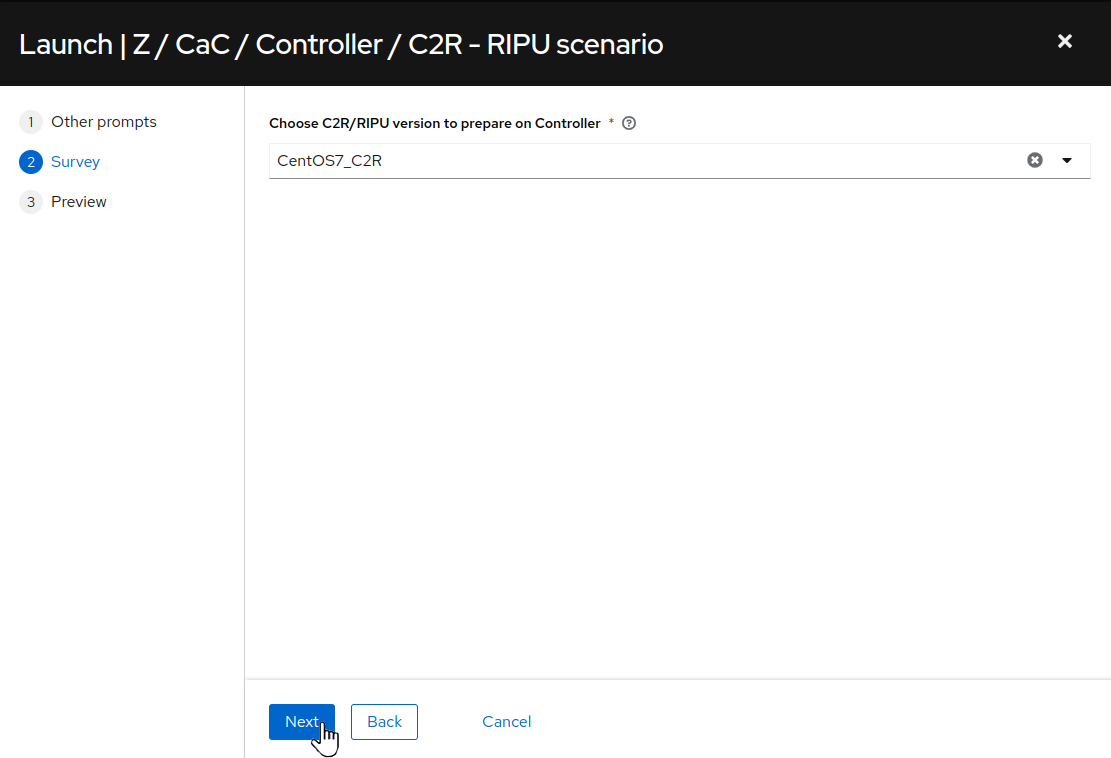
-
Review the preview job dialog then click
Launch: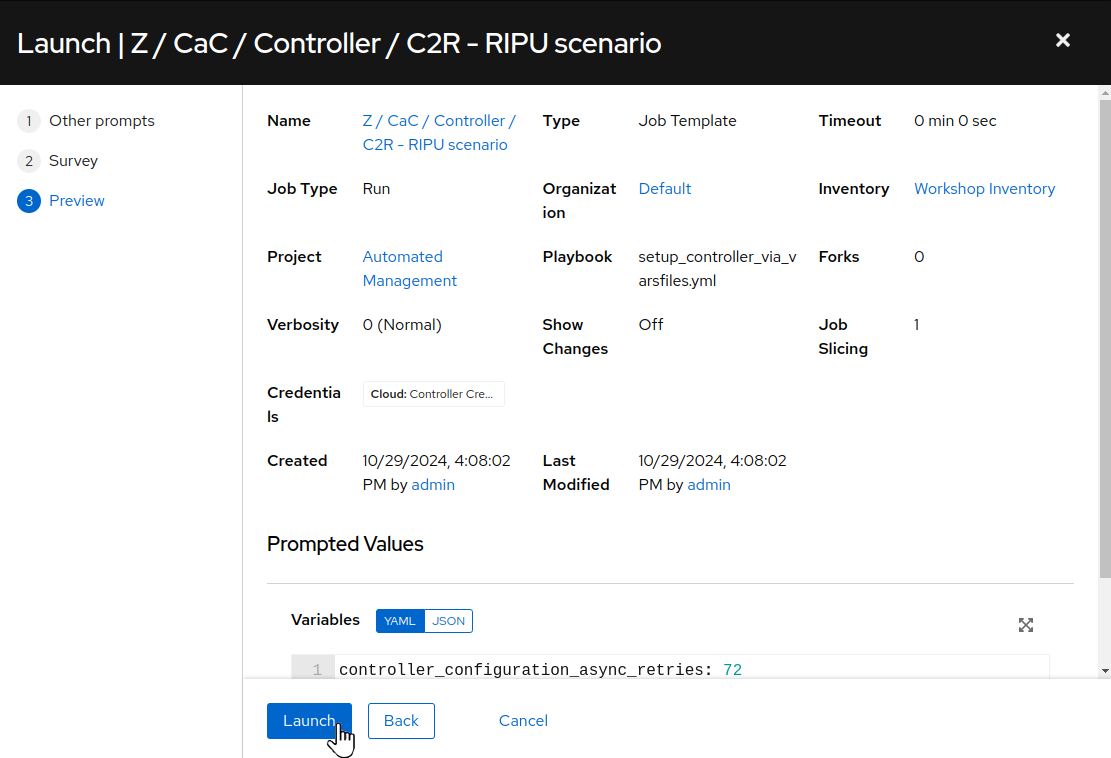
-
Verify that the job run is successful via the job output:
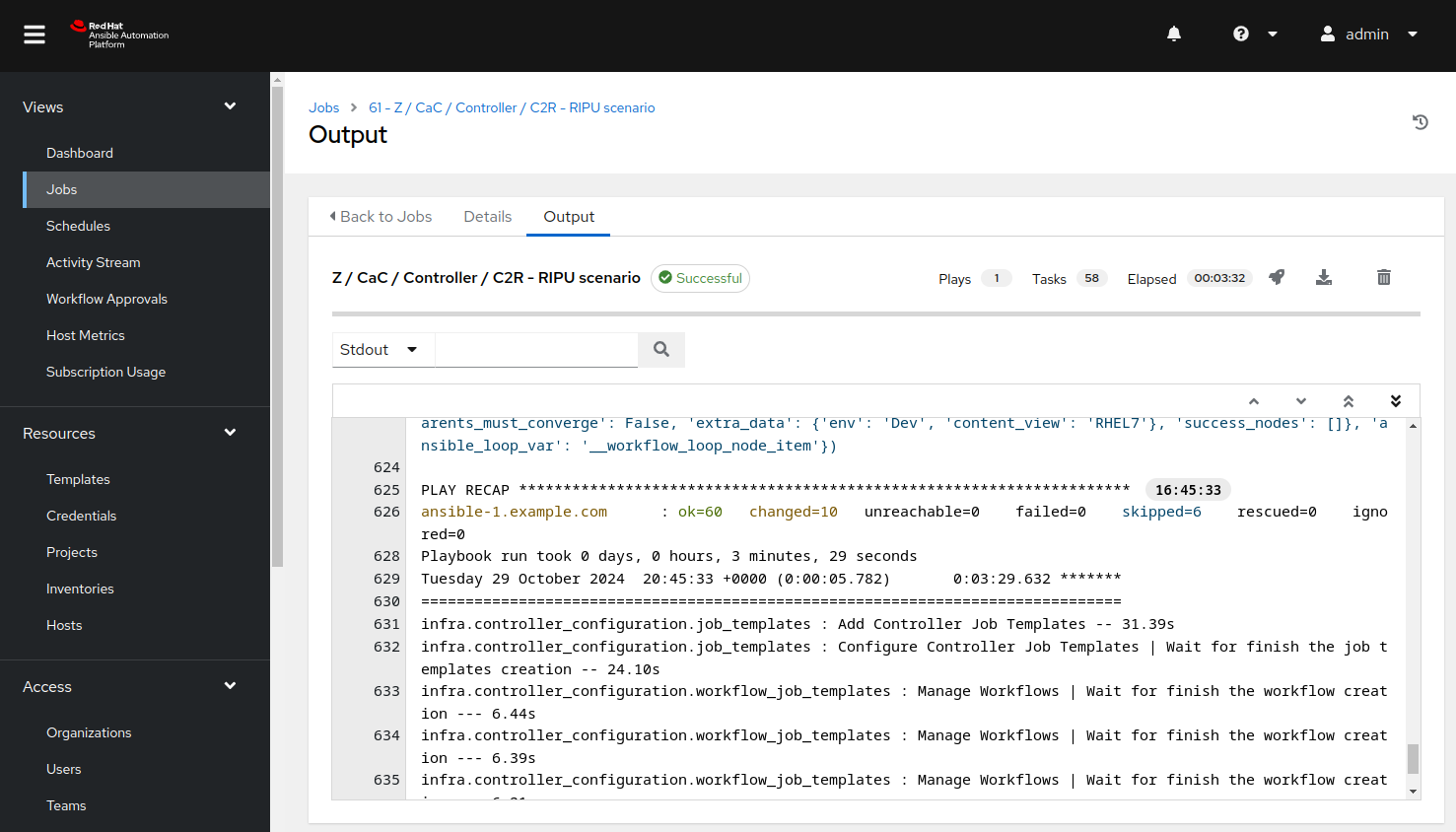
Step 2 - Access the Visual Studio Code Web UI
We will use Visual Studio Code (VS Code) as it provides a convenient and intuitive way to use a web browser to edit files and access terminal sessions. If you are a command line hero, direct SSH access is available if VS Code is not to your liking. There is a short YouTube video to explain if you need additional clarity: Ansible Workshops - Accessing your workbench environment.
-
You can open VS Code in your web browser using the “Console URL” link under “Visual Studio Code” on the workshop landing page. The password is provided below the link. For example:
-
After opening the link, type in the provided password to access your instance of VS Code.
Note
A welcome wizard may appear to guide you through configuring your VS Code user experience. This is optional as the default settings will work fine for this workshop. Feel free to step though the wizard to explore the VS code bells and whistles or you may just skip it.
Step 3 - Open a Terminal Session
Terminal sessions provide access to the OS commands and utilities that will help us understand what’s going on “behind the curtain” when the CentOS conversion automation is doing its thing.
-
Use VS Code to open a terminal session. For example:
-
This terminal session will be running on the AAP control host
ansible-1. Next, use thesshcommand to login to one of your CentOS hosts. Finally, use the highlighted commands confirm the CentOS version and kernel version installed.For example:
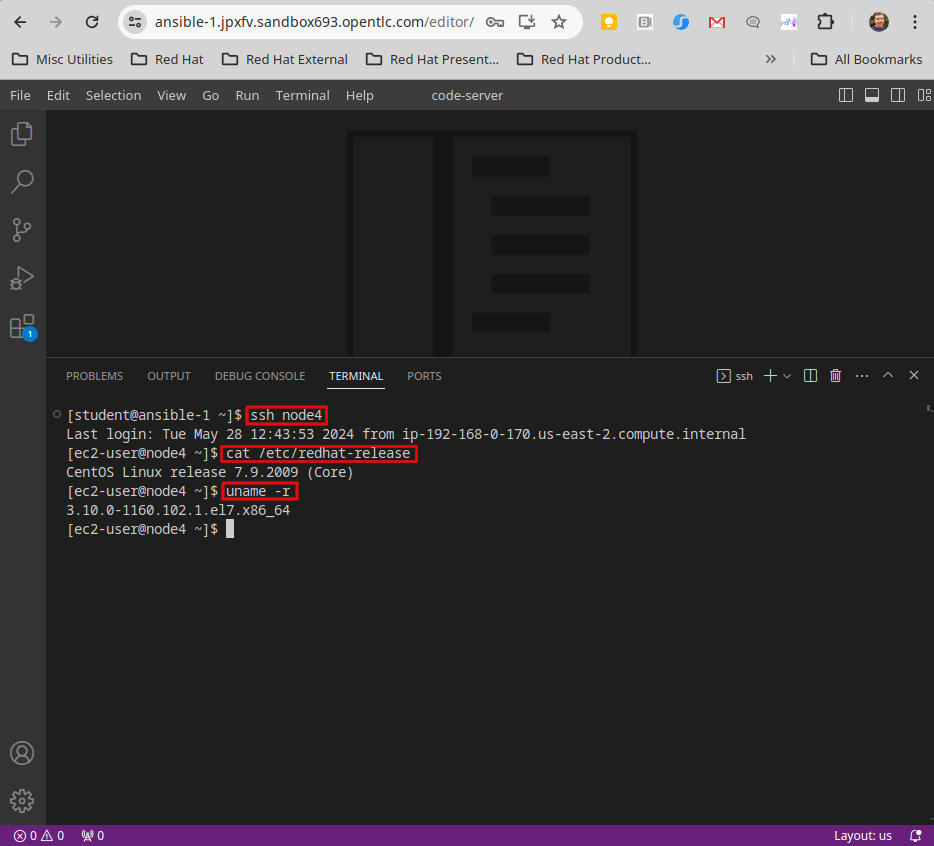
-
In the example above, the command
ssh node4connects us to a new session on the node4 host. Then the commandscat /etc/redhat-releaseanduname -rare used to output the OS release informationCentOS Linux release 7.9.2009 (Core)and kernel version3.10.0-1160.102.1.el7.x86_64from that host.
Step 4 - Access the Satellite Web UI
The Satellite Web UI is where we will go to review the Lifecycle Environments, Content Views and Activation Keys configured on the Satellite, as well as tracking the status of the CentOS hosts as we proceed through the conversion workflow through to when they become RHEL hosts.
-
Let’s open the Satellite Web UI in a new web browser tab using the “Console” link under “Red Hat Satellite” on the workshop launch page. For example:
-
Enter the username
adminand the password provided. This will bring you to your Satellite Web UI dashboard like the example below: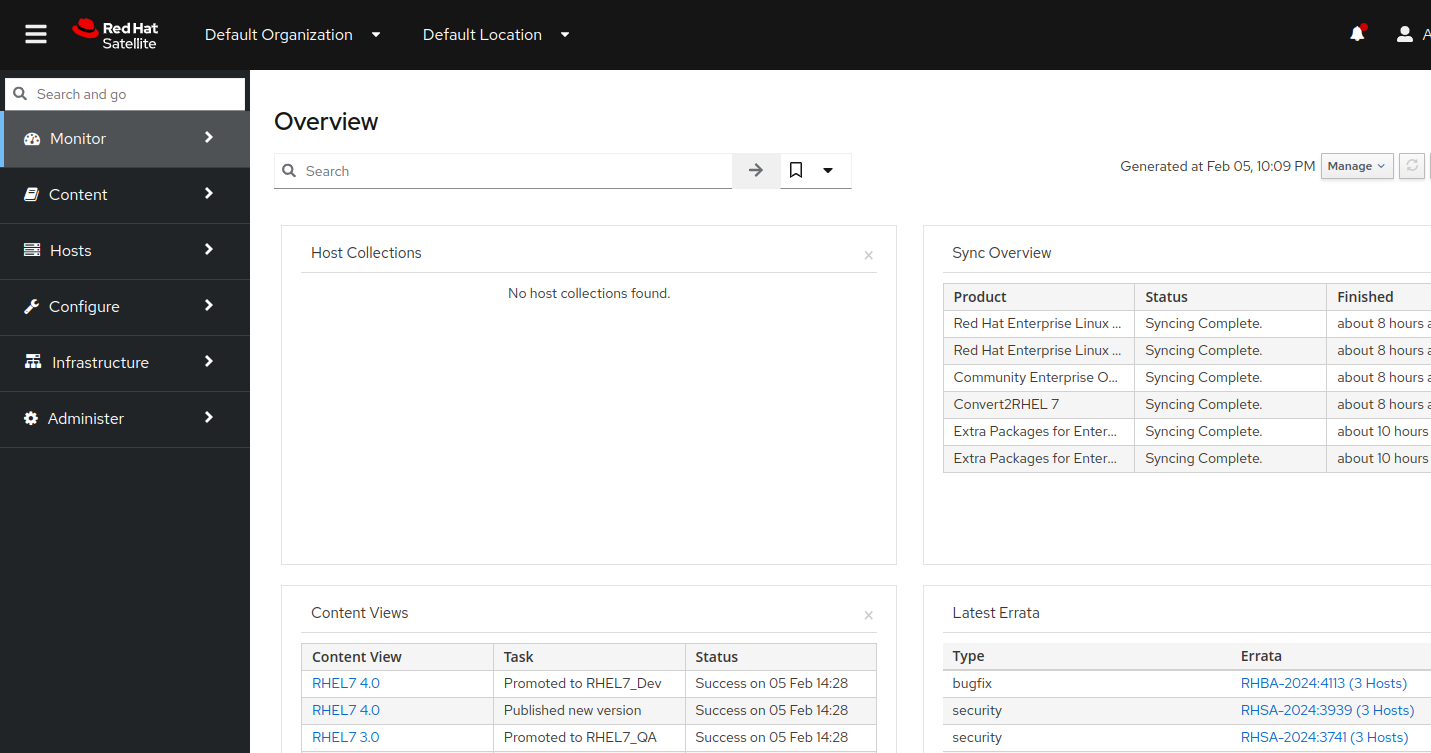
Step 5 - Access the Web Console
We will use the Web Console to review the results of the Convert2RHEL pre-conversion analysis reports we generate for our three-tier app servers.
-
Open a new web browser tab using the link under “RHEL Web Console Interactive Server Admin Interface” on the workshop launch page. For example:
-
Enter the username
studentand the password provided. This will bring you to a Web Console Overview page like the example below: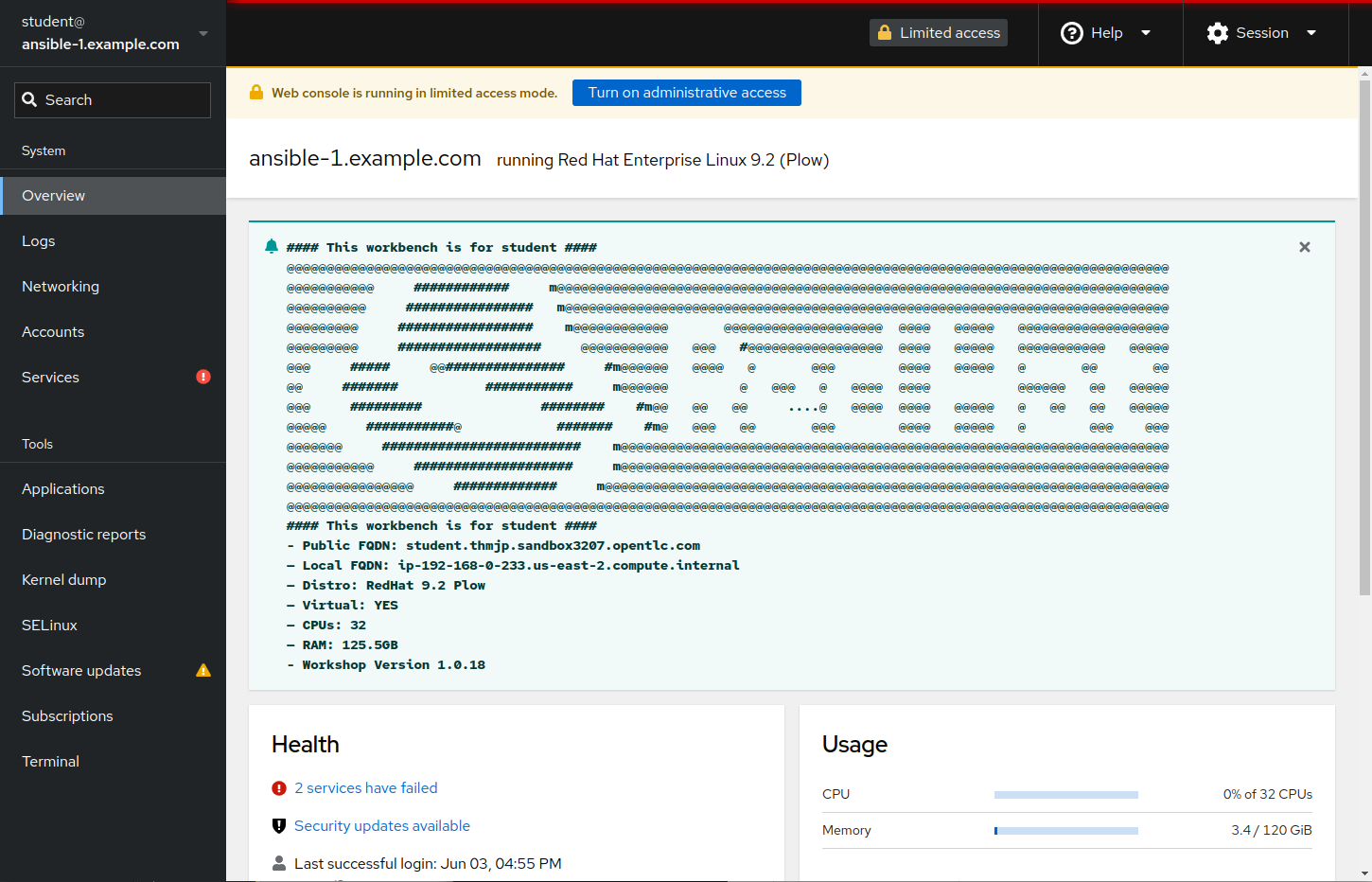
-
We will revisit the RHEL Web Console when we are ready to review our pre-conversion reports in an upcoming exercise.
Step 6 - Challenge Labs
You will soon discover that many exercises in the workshop come with a “Challenge Lab” step. These labs are meant to give you a small task to solve using what you have learned so far. The solution of the task is shown underneath a warning sign.
Conclusion
In this exercise, we learned about the lab environment we will be using to continue through the workshop exercises. We verified that we are able to use VS Code in our web browser and from there we can open terminal sessions. We verified access to the AAP Web UI which will be the “self-service portal” we use to perform the next steps of the CentOS conversion automation workflow. We also made sure we are able to access the Satellite Web UI where we can review the repositories providing the packages for the CentOS conversion automation workflow, as well as the status of the hosts themselves. Finally, we connected to the RHEL Web Console where we will soon be reviewing pre-conversion analysis reports.
Use the link below to move on the the next exercise.
Navigation

